



Next: Preliminary Questions
Up: Op-Amp Basic Concepts
Previous: Gain with Feedback (Closed
Figure 5.7:
Basic Op-Amp
 |
- 1.
- Set up the circuit in Fig.5.7.
- 2.
- Measure the DC values at the points indicated with an 'X'.
Calculate the values theoretically and compare them with the measured ones.
- 3.
- Input a sine wave of amplitude 0.03V into Q1.
at a frequency of about 50KHz.
Measure the open loop voltage gain Adm.
Calculate the theoretical value for the gain
and compare it to the measured result.
- 4.
- By varying the amplitude of the input signal, measure the maximum swing
of the circuit. What happens at the output when the input signal becomes too large.
- 5.
- By driving several different resistor loads ranging from
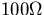 ,
to 100K, determine the output resistance
of this circuit.
Compare your measured value with the theoretical one.
Also, compare the measured value here with the
measured value of the diff-amp in the previous
experiment.
,
to 100K, determine the output resistance
of this circuit.
Compare your measured value with the theoretical one.
Also, compare the measured value here with the
measured value of the diff-amp in the previous
experiment.
- 6.
- Connect the feedback as indicated in Fig. (5.5). Use resistance values
of 10K and 1K for RF1 and RF2 respectively, and a
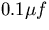 .Measure the voltage gain
and decide if it can be represented by equation (5.35).
.Measure the voltage gain
and decide if it can be represented by equation (5.35).
- 7.
- By driving various loads like you did above, try to determine the output
resistance of the circuit with feedback.
How does feedback affect Ro?




Next: Preliminary Questions
Up: Op-Amp Basic Concepts
Previous: Gain with Feedback (Closed
Neil Goldsman
10/23/1998
