This is an old revision of the document!
Overall Average SA/Lipid
(author: Xiaohong Zhuang)
If you are looking for multi lipid system, go to bottom.
Note: The gnuplot assumes you have standard truetype fonts. If you are doing analysis on DT2. Add the following to your .cshrc.mine file:
# modify the environment by add it to the font search path setenv GDFONTPATH /local/X11/fonts/TrueType
1. The brief instruction to obtain and plot SA/lipid of single lipid system
Example of analysis: e.g._sa_1_lipid.xlsx
This scripts that you need to calculate single lipid surface area per lipid using the gzip file: area_1_lipid.gz
DT2 path: /lustre/ewang125/scripts/area_1_lipid
1. Copy the folder area_1_lipid from the path highlighted above to your directory has contains all dyn files
1.1 Update the 100 (or 36 if using the *.gz file not DT2 files) in area2.scr (line 23) to your value for the # lipid per leaflet
2. Go to the area_1_lipid folder and run the following scripts in PuTTY command line.
2.1. It is used to calculate the surface area per lipid starting from beginning (all dyns). Run the script by command: 1_run_area.scr
in order to find the dyn that the system reaches equilibrium. The key steps of 1_run_area.scr file are shown below:
# To make files executable
chmod u+x area2.scr,
chmod u+x area-block.exe
# Run area2.scr to obtain the area starting from beginning in time step
area2.scr
# Convert times steps to ns (Assume 2fs/step), and calculate the cumulative (running) average of surface area/lipid, which is the average of all the existing area data
awk '{time=($1)*0.000002} {printf "%i\t%2.3lf\t%.2lf\t%.2lf\n",$1,time,$2,(p+=$2)/NR}' area_all_ns.dat > area_time_acc.dat
# Generate the data file with reduced the number of the data points (1/50 of original) for plotting in excel.
# The purpose of the reduction of data points is to avoid Excel clash to loading larger data points.
sed -n '1~50p' area_time_acc.dat > area_time_acc_excel.dat
After run 1_run_area.scr, the files area_time_acc.dat and area_time_acc_excel.dat will be generated. For area_time_acc.dat, the first column is time in nanosecond (ns), the 2nd column is the surface area per lipid at each time (step), and the 3rd column is the cumulative average of surface area per lipid.
2.2. Generate the plot of area vs. time in order to find the dyn that the system reaches equilibrium
2.2.1. If you are using WinSCP, you may run the script by command: 2_plot_sa.scr to use Gnuplot to generate plot 2_sa.tif. And then you can open and view the image in WinSCP by right-click on the file. Plot using Gnuplot I personally think is convenient in the linux system but it is optional. An example of the plot is shown below.
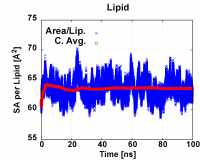 Figure 1. Example surface area per lipid plot
Figure 1. Example surface area per lipid plot
2.2.2. If you don’t use WinSCP,or if you are not comfortable with Gnuplot, you can also use Excel to plot area_time_acc_excel.dat in Excel. The example of the plot in Excel is attached.
Based on the area plot, we can determine when (at which dyn) the system reaches equilibrium. The equilibrium dyn number is the dyn file number that your cumulative (or running) average surface area per lipid (sa/lip) (red data points in Fig.1) becomes constant for around 20-30ns (i.e 10-15 dyn, refer to note). Since the running average including the beginning high values,we will also determine equilibrium based on the area per lipid (blue data points in Fig.1) that fluctuate around the same center line).
e.g. For in Fig.1, the cumulative average area (red) indicate that system reach equlibrium at around 30ns, and the areas (blue) fluctuate around the same center line, so we use the data from 50-100ns (dyn 26-50) or 60-100ns(dyn 31-50) to calculate the average area/lip.
3. Based on equilibrated dyn range on step 2, select the data points from equilibrated dyn to the end to calculate the block-average surface areas. 3.1 In 3_cal_avg_std.scr, please update the total number of last dyn*.dcd files to calculated the averages.
set Ndyn = 20
The example states that you want to do the averages from the last 20 dyn*dcd files. Let's say you have 50 dyn*.dcd files, then the first 30 files are ignored. If each file had 2ns of data, then you are calculating the average from 60-100ns.
# This following command calculates the block average, the output file name (area_avg_std.dat) and the block size (1000) in time steps i.e. each dyn is treat as a block
3.2 Calculate the block-average surface areas by command: 3_cal_avg_std.scr
# Store the output file name (area_avg_std.dat) and the block size (# of steps in a DCD file=Ndata) in time steps into a file area-block.inp, which is the input data file for area-block.exe
echo area_avg_std.dat $Ndata > area-block.inp area-block.exe < area-block.inp
Note: For #define MAX_R 100000 in area-block.c, you might have to change the number to a larger one (larger than your # data points) and recompile it.
As you can see, the output average area data are saved in area_avg_std.dat. The result is given in average+- population standard deviation.
4. Calculate averages, sample standard deviation, and standard error of block averages by command: 4_run_calc_stderr.scr
The file avg_stderr.dat will be generated that will show the final values that we need, which are the average of the block averages and the standard error of the block averages, i.e. SA_avg/lip +- Standard error. You may refer to the attached Excel file which also demonstrate how the standard error is calculated if you are interested.
Note: The corresponding nanosecond are based on the “number steps” and “timestep” that we set. For example, in the dyn-2.inp file, we see there a code line: “numsteps 1000000 ; # run stops when this step is reached”
and another code line:
timestep 2.0 ;# fs/step
So you multiple 2fs/step with 1,000,000 steps per dyn file, which makes is 2ns per dyn file. (since 1fs=10^(-15) s, 1ns==10^(-9) s )
Get the equilibrium data (test)
(author: Yalun Yu, email: alanyu17@terpmail.umd.edu / yalun.research@gmail.com)
< Email me if anything is wrong >
This is a brief instruction to obtain the time range of equilibrium (and also the minimum block size can be used for standard error calculation). Based on these, calculation of SA/lipid and Ka is done automatically for your lipid only system. Run Xiao's 1_run_area.scr before doing this. Please put the scripts in the same folder as you run 1_run_area.scr. You will need pymbar package (in python) for this:
1. Install Anaconda (https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/).
a) Download the python3.7 version for Linux [I used the '64-Bit (x86) Installer (652.5 MB)'] and put the .sh installer in your home directory (or any other place you can access and execute it) on DT2. b) make the .sh file an executable (chmod u+x $NameOfInstaller.sh) c) Install by running "./$NameOfInstaller.sh", keep in mind where you have installed it.
2. Make sure the Anaconda installation path is included (see below) in your ~/.cshrc.mine (if using csh) or ~/.bashrc.mine (if using bash) and source the .mine file.
In ~/.cshrc.mine, add this line: set path = ($HOME/anaconda3/bin $path) or in ~/.bashrc.mine, add this line: export PATH="$HOME/anaconda3/bin:$PATH" [may differ depending on where Anaconda is installed, see 1(c)]
3. Install the pymbar package.
conda install -c omnia pymbar
Download the script: area_ka.tar.gz
Change the temperature and number of lipids per leaflet in pymbar_area_ka.scr:
set temp=323.15 set nlip=36
Change the initial guess (or your preference) for block size (in ns) and the steps size (in ns) of your output (usually 1ps):
area_handling.py 10 0.001 >& all.dat
After running pymbar_area_ka.scr, you'll see all.dat, SA/lipid is in angstrom^2 and Ka is in N/m.
