



Next: Emitter Follower
Up: CE Amp Small Signal
Previous: Voltage Amplifier Equivalent Circuit
- 1.
- Construct the circuit in Fig. 2.10.
Notice that it is really
just the CE amp of Fig. 2.6, driving a load of RL=1K,
and being driven by a voltage source with source resistance
RS=10k.
- 2.
- Using the expressions above, theoretically determine
the voltage gain of the circuit.
- 3.
- Measure the voltage gain
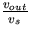 under the same input voltage and frequency conditions
as in Exp. 2.4.2. Compare the measured gain with
your theoretical result.
under the same input voltage and frequency conditions
as in Exp. 2.4.2. Compare the measured gain with
your theoretical result.
- 4.
- Try two different values for the load resistor: let RL=5K
and RL=10K. From the output voltages measured for the
different values of RL determine the output resistance
of the CE amp Rout. Compare the value with the
theoretical one.
- 5.
- Replace RL with its original value of 1K. Now,
measure the AC voltage at the base.
Now repeat your measurement with
two different values for the source resistor: let RS=5K
and RS=10K. From the base voltages measured for the
different values of RS determine the input resistance
of the CE amp Rin. Compare the value with the
theoretical one.




Next: Emitter Follower
Up: CE Amp Small Signal
Previous: Voltage Amplifier Equivalent Circuit
Neil Goldsman
10/23/1998